Government type
Constitutional monarchy (parliamentary democracy)
Parliament
Bicameral parliament (Senate and House of Representatives)
Trade balance
Exports: RM 935.4 billion (2017)
Imports: RM 836.4 billion (2017)
Main exported/imported goods
・Main export goods: electronic equipment, palm oil, chemicals, petroleum and petroleum products, liquefied natural gas, machinery and tool products, metal products, scientific and optical instruments, rubber products, etc.
・Main import goods: electronic equipment, manufacturing equipment, chemical product, transport equipment, metal products, petroleum and petroleum products, iron and steel products, scientific and optical instruments, food, etc.
Number of foreign visitors
26.10 million (2019)
Administrative divisions
13 states and 3 federal territories
System of government
Malaysia is a federal constitutional elective monarchy. The Head of State is systematically rotated among the nine hereditary rulers of the Malay states (Conference of Rulers) for a five-year term. Executive power is vested in the Cabinet, led by the Prime Minister as the Head of Government. The Constitution stipulates the position of the Yang Di-Pertuan Agong (King) as the Head of State, and authorities of executive, legislative and judicial branches. As for local government, each state has its own constitutions, and the Federal Constitution only gives provisions concerning the heads of the states including sultans who are hereditary rulers of the states and governors appointed by the King, and the authority of the legislative assemblies. Details are stated in the constitutions of each state.
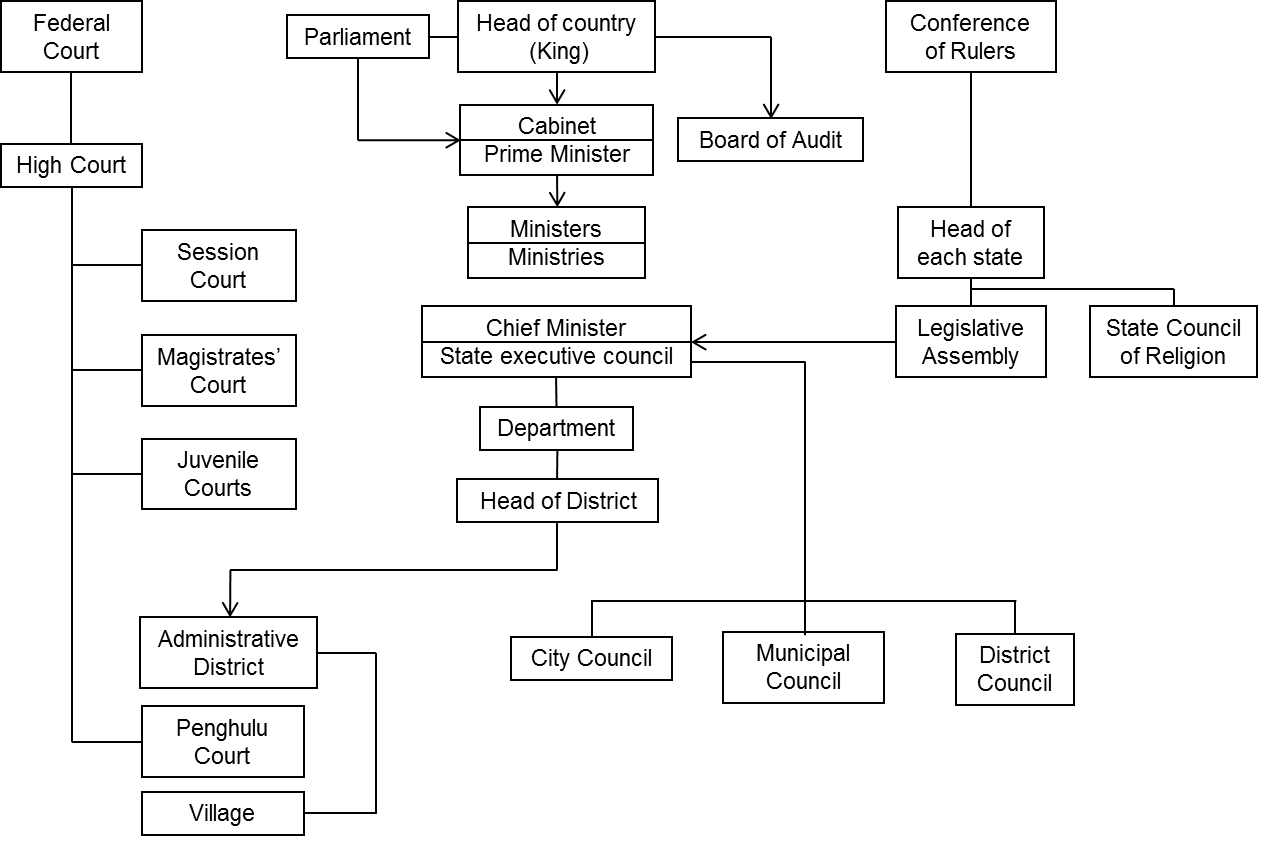
Sources: Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan Website, Tourism Malaysia Website, “Local Administration in ASEAN Countries” (Council of Local Authorities for International Relations, February 27, 2004), “CLAIR REPORT NUMBER 313” (December 10, 2007), UNWTO HP ”Tourism Highlights, 2012 edition”
(As of January, 2021)